4 Car Loan Terms You Need to Know
Owning a car in Singapore is an uphill task due to the additional fees you’ll have to pay. Fortunately, there are financing options, i.e. car loans that you can apply for to ease the finances. The process of acquiring a car loan, however, is a pretty daunting task, especially if you are a first-timer. You’ll need to first understand the typical car loan terms used during application.
In this article, we’ll be touching on typical car loan terms like car loan-to-value ratio, credit score and more!
1. Interest Rate

It’s important to know in Singapore, you will not be able to get 100% financing for your car. Most of the time, only 30% – 50% financing is available. MAS has also capped the financing level of cars with an open market value (OMV) of $20,000 or less at 70%, while those with OMVs of more than $20,000 can borrow up to 60% of the car open market value.
When you decide that you’ll take the loan application, financiers will charge you an additional percentage on top of your loan amount, i.e. the interest rate. The interest rate varies from one financier to another. You should find an interest rate you can comfortably pay off within the payment period. The interest rate may also be dependent on your credit score and the prevailing market factors. Usually, the interest rates are compounded annually for the period of the tenure. In Singapore, the interest rate for car loans varies between 2-4%.
2. Loan Tenure

The next car loan term you’ll need to know is loan tenure. It is the period where you’re expected to clear off the loan amount. There are two categories in this section: short term and long term. Short term offers a tenure of 0-3 years in which the balance, including the interest accrued, has to be cleared off. Usually, the interest rate is lower. On the other hand, long term tenures can last up to ten years and offer more flexible payback amounts. In Singapore, MAS capped the maximum tenure at seven years.
3. Credit Score
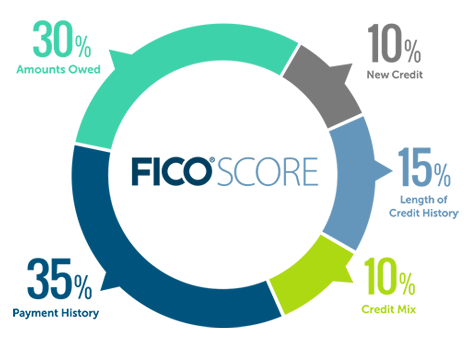
When seeking car loans, banks have no obligation to offer you the maximum financing level, i.e. 70% financing level for cars with OMV of $20,000 or less, or 60% financing level for those with OMVs of more than $20,000. Your credit score will hence determine the financing level you will receive. If you have a poor credit score, the bank will most likely lower your financing level, and if your credit score depicts critical issues such as loan defaulting, you may be denied the car loan altogether. Factors which will lower your credit score include late remissions, unsecured payments and even having past debts written off. Conversely, a higher credit score means higher financing level for your car loan. It is important that you build your credit score before you consider taking a car loan.
4. Loan-to-Value Ratios

The loan-to-value ratio is a metric used to assess the risk involved in offering you a loan. It takes into account the loan amount and your credit score. If you have a poor credit score and would like to borrow up to $16,000, the financing institution considers this as a high risk. With this classification, they would assess whether it is feasible to forward the car loan to you at the determined interest rate. The acceptance or rejection of this risk is highly dependent on your credit score, or even providence of security for the loan.
People also liked: A COMPLETE GUIDE TO DISINFECT YOUR CAR 10 THINGS WE LOVE ABOUT CAR SUBSCRIPTION COVID-19 CIRCUIT BREAKER: IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR CAR OWNERS




