Safety Considerations While Buying A Car
A car is judged Safe in terms of its structural crashworthiness, occupant protection and accident avoidance technologies.
Safety remains a top concern for consumers and fortunately present day cars offer more occupant protection capability.
Governments and insurance agencies of respective countries perform a variety of tests on each vehicle to determine its performance and some models stand out while others do not. Reliability Ratings show how well vehicles have held up compared with competitive models.
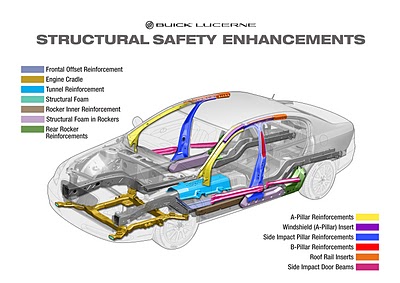
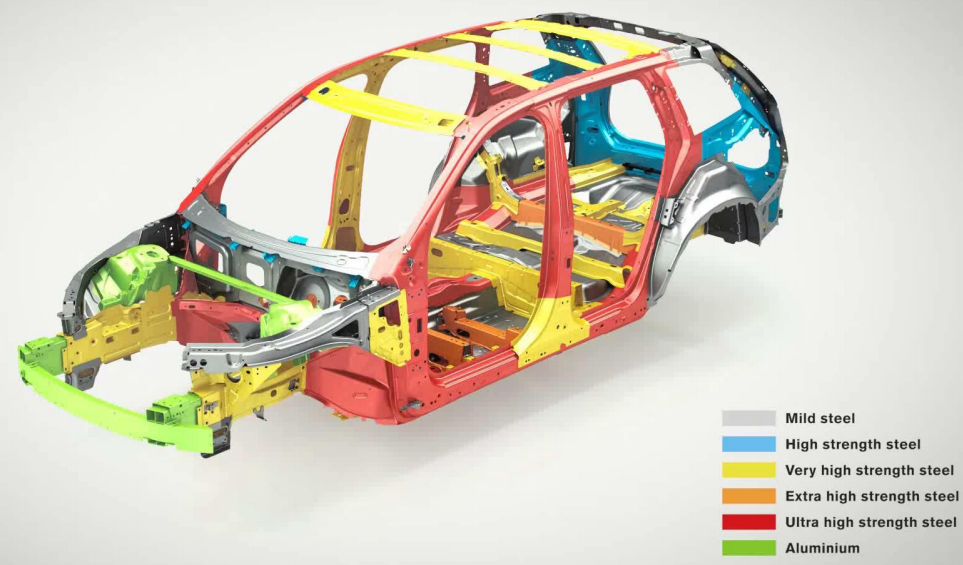
STRUCTURAL CRASHWORTHINESS:
A crash test is performed to ensure safe design standards in crashworthiness.
Front, Side, Rear, Rollover impact crash tests are conducted and star ratings are provided for all tested models and published on the agencies websites.
Front and Rear Impact protection:
Current generation cars protect occupants in frontal, rear and offset crashes by using crumple or crush zones to absorb crash energy. This means that the structural members of the car absorb the impact of the crash, not the occupants.
Side impact protection:
In the case of side impact, protection can be improved with increased side door strength, internal padding using energy absorbing foams and improved seat design.
Rollover Impact protection:
A rollover occurs when a vehicle tips over onto its side or roof. Rollovers have a higher fatality rate as compared to other types of vehicle impacts. The intent of rollover protection is to prevent occupant injuries and ejection during a rollover crash.
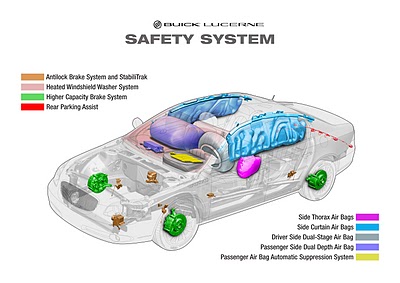
OCCUPANT PROTECTION:
Occupant safety can be ensured using restraint systems such as seatbelts, airbags and head restraint systems.
Safety seatbelts are a necessary safety feature in a car. Current generation 3 point seatbelts have pretensioners. During the crash event, these tighten the seatbelt by removing the slack in it. They additionally have load limiters which help in controlling the movements of occupants by releasing the seatbelt gradually.
An airbag is a vehicle safety device to prevent vehicle occupants from hitting hard components in the car during crash. The airbag module is designed to inflate extremely rapidly then quickly deflate during the event of collision.
Variety of airbags exist in current generation cars among which driver and passenger frontal airbags are most common. Recent advancements include side torso-protecting airbags, knee airbags and side curtain airbags.
Active head restraints:
In the event of a rear crash, the seat reacts by the moving head restraint forward. It also performs other actions to reduce the risk of whiplash sort of injuries.
ACCIDENT AVOIDANCE TECHNOLOGIES
Several factors contribute to a vehicle’s accident-avoidance capability, with the two most important being braking and emergency handling. Lab tests data, Consumer Reports provide an accident-avoidance rating on all tested vehicles.
Few of these technologies are mentioned below:
Forward Collision Warning Systems:
Front sensors detect an impending crash and automatically deploys safety devices such as seatbelt pretensioners and airbags. This technology warns the driver of an impending collision so that the driver can brake or steer to avoid the collision.
Automatic Emergency Braking:
This technology works with Forward Collision Warning to help the driver in dodging a crash with another vehicle or object by consequently applying the brakes.
Lane Departure Warning Systems:
Utilizing a camera framework to track a vehicle’s position in connection to lane markings on the street, this technology cautions the driver of unintentional lane shifts.
Rear view Video Systems:
This technology helps the driver see behind the vehicle with backup cameras to avoid backing over people or objects when moving in reverse.




